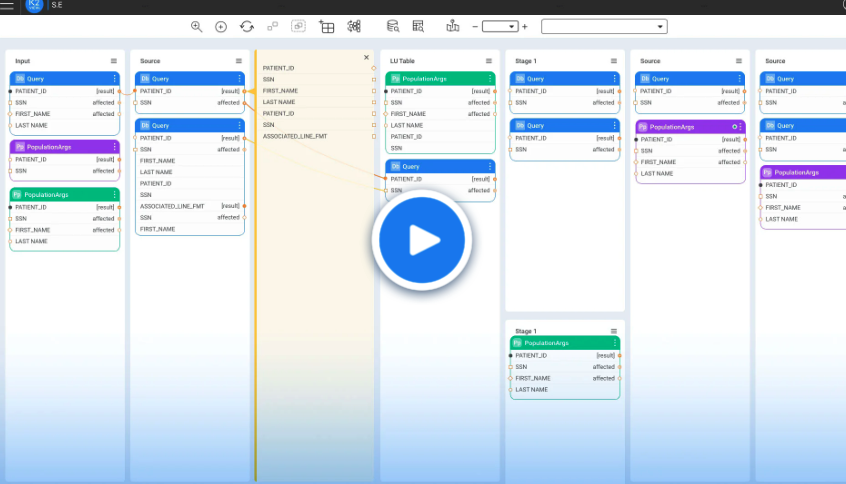
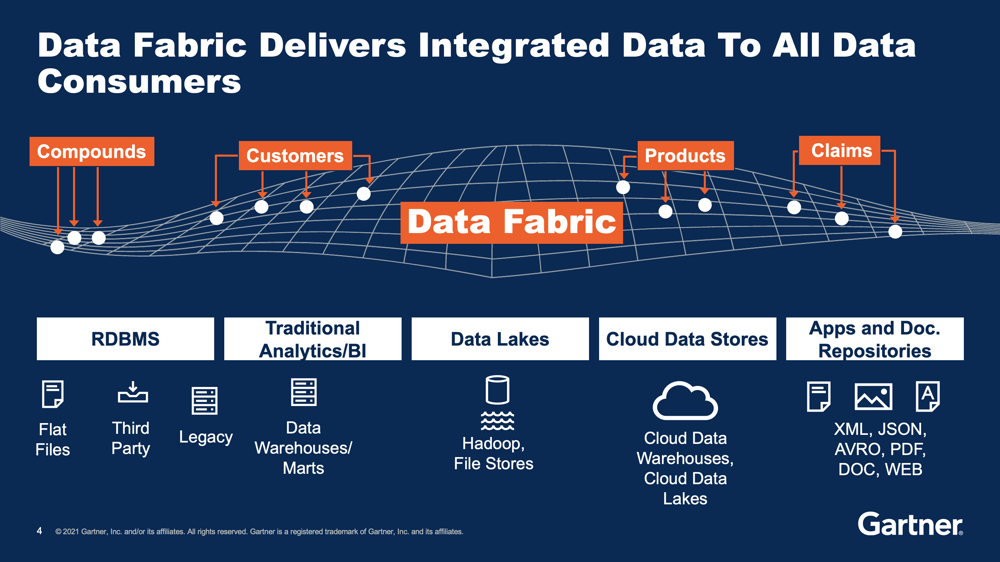
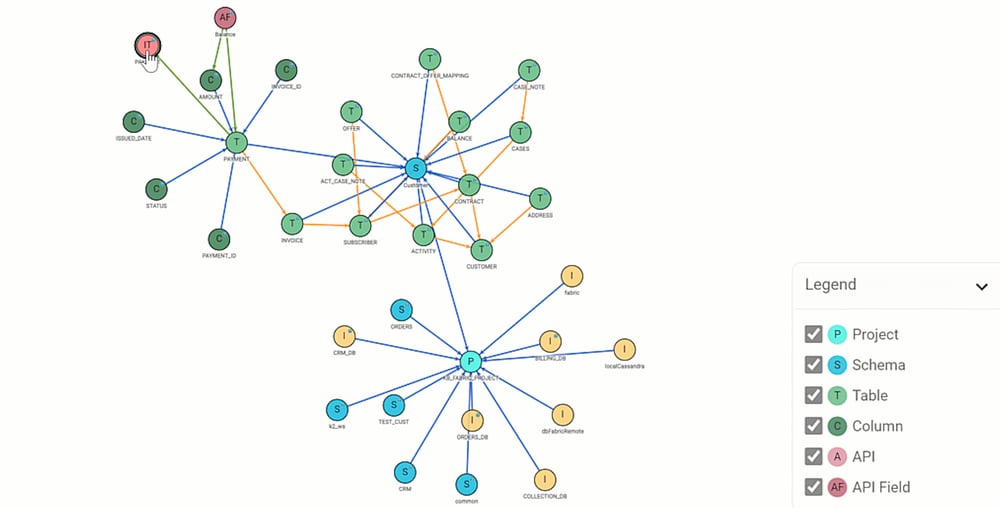
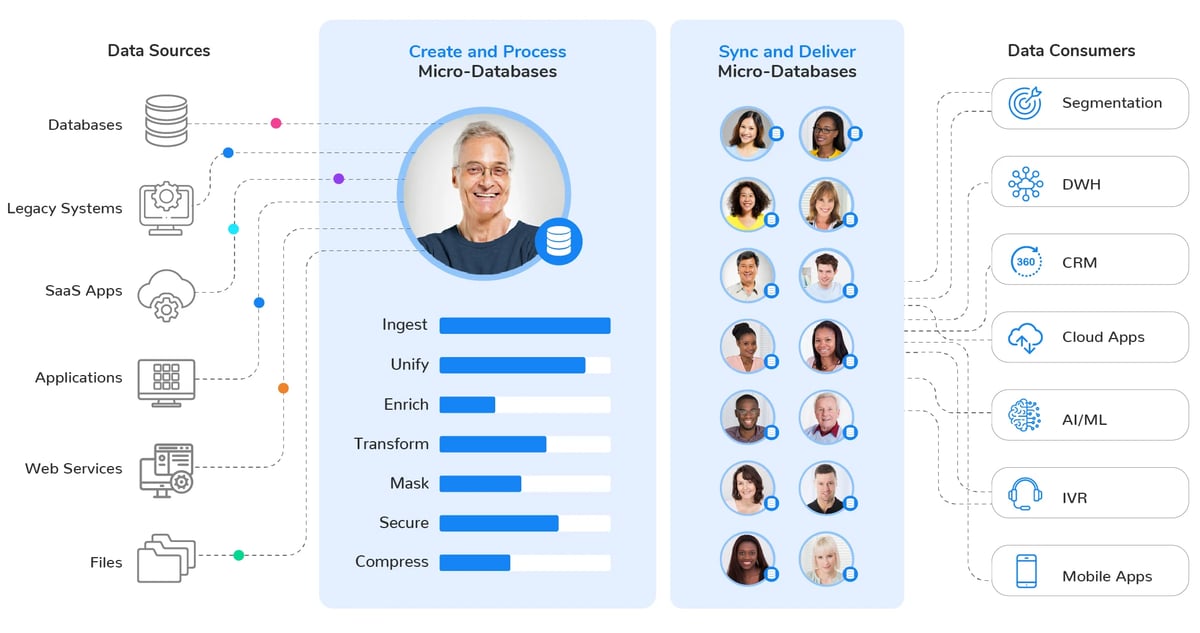
Platform
Capability
Architecture
Solutions
Initiative
Industry
Company
Company
Reach Out
Resources
Resources
Education & Training