This article explains "What is Cloud Data Integration?" and goes on to discuss its benefits, challenges, requirements, and a novel Enterprise iPaaS Platform based on data products.
Table of Contents
What is Cloud Data Integration?
6 Benefits of Cloud Data Integration
The Biggest Challenge of Cloud Data Integration
Support for Key Integration Patterns
Enterprise iPaaS Platform Checks Every Box
Data Products Raise iPaaS to a New Level
Take a Business-Minded Approach to Cloud Data Integration
What is Cloud Data Integration?
As enterprises increasingly embrace multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, critical data is now dispersed across multiple cloud sources, making it difficult to access. Today, there’s a rising need among enterprises for cloud data integration.
Cloud data integration refers to the consolidation and movement of data originating in disparate systems, whether on premises or in the cloud, to a target system. The goal of integrating this data is to make trusted data easily accessible by all authorized data consumers – for operational and analytical workloads.
With the right data integration tools, enterprises can ensure their cloud-based and on-premise applications consistently synchronize valuable data, and deliver it to data consumers who can use it to produce better business outcomes.
6 Benefits of Cloud Data Integration
What is cloud data integration, if not Integrating applications and data across various types of cloud environments (private, public, or multi-cloud)? When run on-premise systems, cloud data integration provides enterprises numerous benefits, including:
-
Simplified integration
A cloud-based approach to data integration provides a unified and streamlined infrastructure for managing all current and future integrations. Instead of taking a patchwork approach to integration, a cloud-based solution makes it easier to quickly integrate new source systems, and provide a holistic view of data. -
Ease of use
Cloud data integration allows you to easily create and manage scalable data pipelines, between source and target systems, for both operational and analytical use cases. -
Cost savings
Integrating your data through the cloud frees enterprises from the burden of buying, installing, and operating integration hardware and software. They also no longer need to dedicate costly developer hours to generating code for custom integrations. -
Increased scalability
Cloud data integration enables your organization to more easily manage increasing data and workflow volumes without worrying about manual data entry, execution of SQL queries, or other time-consuming tasks. -
Greater business agility
Cloud data integration leads to increased flexibility, faster time to market, and more agile application development. -
Easier data governance and security
Cloud data integration allows for quick compliance with increasingly stringent data governance standards and data privacy regulations – via workflows that standardize data storage and management.
The Biggest Challenge of Cloud Data Integration
Like all technological advancements, cloud data integration presents considerable challenges, alongside its many benefits.
Designing data integration flows across source and target systems, scaling data and computing capacity, proving data governance to regulators and customers, and educating non-technical business users on how to leverage data, are just some of the common challenges that must be addressed.
However, the most significant challenge of cloud data integration arises long before deployment – it’s choosing the right cloud integration platform.
Ideally, your company will deploy just one integration platform to serve all of your integration needs and use cases. But as the category of cloud integration tools expands, choosing the solution that fits you best is often a complex process in and of itself.
Support for Key Integration Patterns
Analyst firm Gartner reinforces the advantages of cloud-based integration by assessing different data integration platforms based on a framework of integration patterns.
According to Gartner, every integration need – even the most complex of tasks – can be reduced to a combination of 3 basic integration patterns: Data Consistency, Multistep Process, and Composite Service.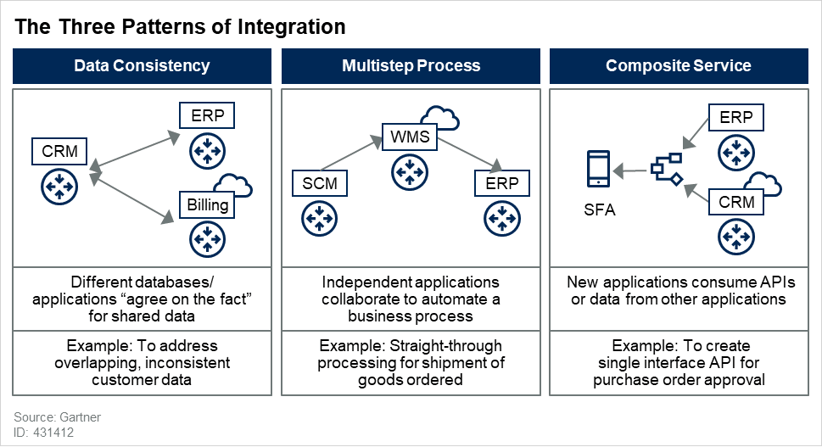
Gartner: All integration challenges can be decomposed
into some combination of three integration patterns.
The 3-pattern framework helps data teams determine which integration patterns are most relevant to their company, and understand which capabilities are required to fulfill them.
|
Description |
Requirements |
|
|
Data consistency |
Data consistency refers to the need to ensure all of your data products (individual business entities, such as customers, products, suppliers, etc.) are in sync across all relevant databases and applications. |
|
|
Multi-step process |
Multi-step process represents the need to streamline certain business processes across independent applications, by automatically synchronizing activity, and exchanging data. |
|
|
Composite services |
Composite services refer to the need to develop new applications that require access to data in existing systems. |
|
Enterprise iPaaS Platform Checks Every Box
As part of its framework, Gartner assessed 10 categories of data integration tools according to how well they address each of the 3 integration patterns. While most solutions only received a “strong” score on 1 or 2 patterns, integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) is deemed “strong” across the board.
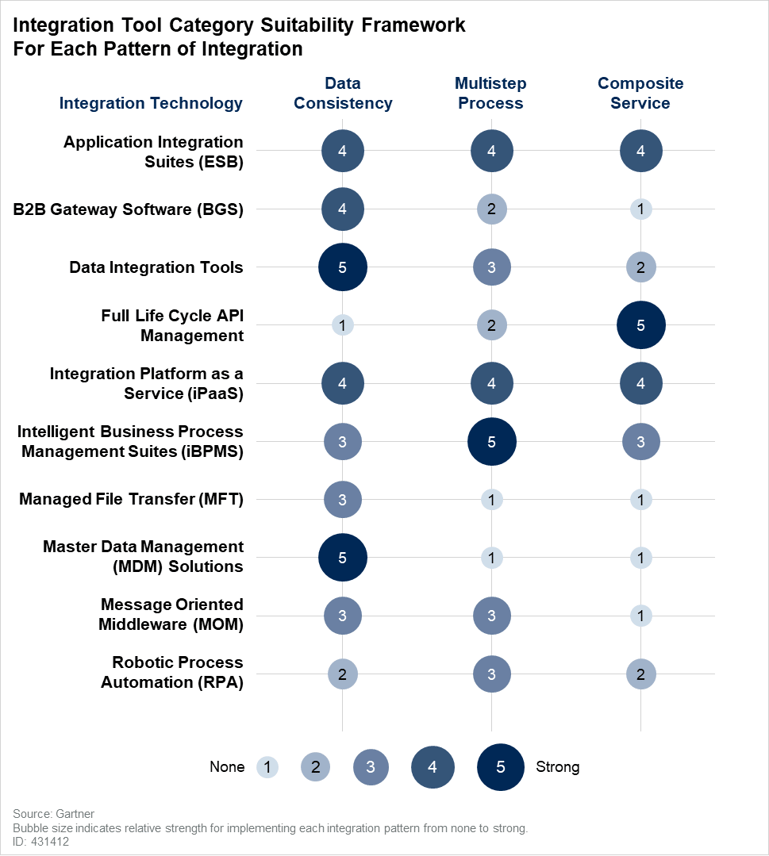 When iPaaS is based on data products, it surpasses every other integration approach.
When iPaaS is based on data products, it surpasses every other integration approach.
iPaaS is a cloud-based integration platform that standardizes how applications and data are integrated in an organization. It connects formerly disparate applications, data sources, and IT environments, to enable real-time and batch exchange of data and processes.
With an Enterprise iPaaS Platform, subscribers can integrate data and applications, with APIs and data integrations involving both cloud-resident and on-premise endpoints. It enables the creation of a unified, cohesive IT infrastructure that streamlines the flow of data across the enterprise, and allows business users to access data on demand.
“iPaaS provides many of the capabilities addressed by ESBs and data integration tools, with an emphasis on addressing cloud services integration use cases, overall ease of use and SaaS-like delivery.”
Gartner Research Note 431412, refreshed February 2021
Data Products Raise iPaaS to a New Level
Gartner’s framework for identifying the most suitable data integration solution category steers most enterprises toward iPaaS for a good reason. The benefits of iPaaS for cloud data integration are extensive.
However, not all iPaaS solutions deliver the unified, holistic view of enterprise data that data consumers require to derive meaningful insights, make better business decisions, or improve operational efficiency.
Data products, a concept that comes from the data mesh framework, help to remedy this issue.
The objective of a data product approach is to provide every business domain in the enterprise the ability to define, access, and control its own data. A data product typically provisions a dataset for a given business entity, such as a customer, vendor, order, claim, or device - in support of an operational or analytical workload. It integrates, unifies, and synchronizes relevant data from underlying source systems, and makes it instantly accessible to users and systems.
When iPaaS is based on data products, it delivers a trusted, real-time view of business entity data, deploys in weeks, can be scaled up or down, and is built to be flexible and modular. It supports application integration via APIs, and data integration via ETL, streaming, messaging, CDC, and data virtualization.
iPaaS supports a broad range of modern data architectures, including data mesh, data fabric, and data hub, within on-premise, cloud, and hybrid environments.
Take a Business-Minded Approach to Cloud Data Integration
All integration tools today are built to enable at least some of the functionality required to fulfill the 3 integration patterns defined by Gartner. However, the differences between the various tools can significantly impact your ability to fulfill your company’s integration needs.
iPaaS is widely considered to be the ideal cloud data integration solution. But within the category itself, there are additional differentiators to consider.
When your Enterprise iPaaS Platform is based on data products, it’s possible to attain all of the advantages of iPaaS while guaranteeing a simplified user experience, a holistic view of all business entity data, and the ability to make better business decisions in real time.