Table of contents
MCP for SAP enables AI to securely access real-time SAP data and context, improving agentic AI accuracy and data governance across SAP landscapes.
Why do SAP and MCP matter for AI agents?
Many organizations rely on SAP to manage their business operations, from finance and logistics to human resources and supply chain activities. Increasingly, they are exploring the use of AI agents — powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) — to automate tasks, streamline processes, or provide instant insights and recommendations.
But there’s a catch. In most organizations, SAP data is only one part of the bigger enterprise data picture. Information relevant to any business process is often scattered across multiple business applications, databases, cloud systems, and files, both inside and outside of SAP. For AI agents to deliver meaningful answers and actions, they need access to all relevant data, not just data isolated within SAP tables. When data remains fragmented, AI agents can only see a piece of the puzzle, limiting their effectiveness and sometimes leading to inaccurate results.
This is where MCP AI comes in. MCP is an open, standardized approach that enables Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI agents to access up-to-date, well-governed AI-ready data – across SAP and other enterprise systems – on demand, while maintaining privacy, auditability, and control.
Instead of copying or syncing data, MCP makes it possible for AI models to dynamically retrieve exactly the data they need from SAP and other relevant source systems at the time of the user request. This grounded, orchestrated access ensures AI agents are working with the most current and complete SAP-sourced information, while also enforcing privacy and security guardrails to prevent sensitive data exposure.

By connecting SAP systems to AI agents through MCP, businesses can unlock the true value of their enterprise data for advanced GenAI-based use cases.
SAP MCP use cases
Many enterprises are realizing the benefits of connecting SAP data – and data from other business systems – to AI agents using the Model Context Protocol (MCP). By allowing secure, governed, and real-time access to multi-source enterprise data, MCP for SAP helps AI agents drive value across different use cases.
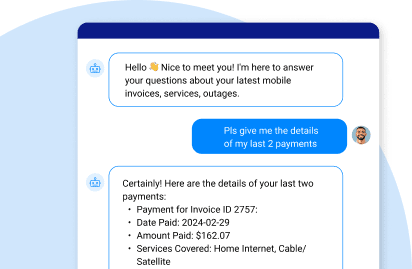
One common use case of SAP MCP is in customer service for industries like telecommunications. For instance, when customers have questions about billing or service outages, the information needed to answer the questions often spans SAP systems (for billing and product data) as well as external customer care applications. With MCP, AI agents can quickly and securely pull up-to-date information from both SAP and other systems, so customers receive accurate answers without delays. At the same time, MCP’s privacy and audit controls help ensure that sensitive data – such as payment information – is protected throughout the process.
Analytics and reporting are also enhanced by MCP for SAP. For example, business leaders often need insights into areas like inventory levels and supply chain status. While inventory data may reside in SAP S4/HANA, freight details might be tracked in a third-party cloud logistics platform, and supplier data could be stored in another system. Using MCP, an AI agent can gather and combine real-time information from all these different sources, presenting executives with a complete and current business snapshot – all through a simple conversational query or chat.
A personalized AI customer experience and automated back-office processing are additional areas where connecting SAP to AI agents is valuable. Imagine a retail scenario where an AI assistant recommends personalized promotions by pulling together purchasing history from SAP ERP and recent website activity logs. Or, in insurance, an AI agent may support automated claims processing by accessing claim details from SAP, CRM records, and scanned claim images – all coordinated and secured through MCP.
According to the K2view State of Data for GenAI survey, only 2% of organizations in the US and UK are ready to deploy GenAI. The main barrier is fragmented enterprise data, especially from core systems like SAP. By tackling these challenges with standards such as MCP, businesses are starting to unlock AI’s real potential – grounded in reliable, multi-source data.
SAP MCP challenges in multi-source landscapes
Enterprise data rarely lives in just one system. While an SAP landscape covers many core business processes, most organizations have important data scattered across several other applications, databases, and cloud services. This fragmentation requires AI agents to communicate with multiple MCP servers, creating major challenges:
Security and privacy
Security and privacy are essential priorities, especially since sensitive business data managed in systems like SAP must always be safeguarded.
When connecting an MCP client to multiple MCP servers, each one linked to a different data source, you must implement guardrails, data governance, access controls, and auditability -- separately in each MCP server.
Fresh data in real time
Stale data can lead to inaccurate suggestions or missed opportunities.
A major hurdle for an MCP server is accessing fresh data from the SAP landscape and connected systems.
To be effective, MCP clients need rapid, real-time access to the latest information, not outdated records from data warehouses or lakes. Because conversational interactions require speed, MCP servers must quickly fetch and process data from multiple sources to keep responses timely and relevant.
Data unification and integration
Retrieving information for AI agents about customers, suppliers, employees, or other business entities means unifying and integrating data from multiple systems like SAP, Salesforce, Workday, and support platforms. Each of these systems would require the implementation of it own MCP server, leaving the cross-system data harmonization to the AI agent.
This means that agentic AI systems must be supported by:
-
Metadata enrichment and semantic layers
-
Entity resolution (master data management)
-
Tooling descriptions and ontology mappings
-
Aggregator layers that unify responses
-
Few-shot examples, chain-of-thought reasoning, and fallback mechanisms
Accurate answers
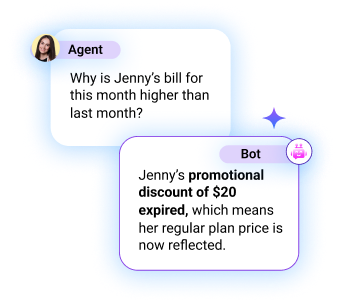
Without up-to-date and unified data access, LLMs may hallucinate answers – generating information that’s plausible but incorrect – based on incomplete or outdated data, or data that lacks utility.
In summary, to address these challenges, generative AI techniques like chain-of-thought prompting (guiding the model step by step), retrieval-augmented generation (retrieving data in data at runtime), and table-augmented generation (querying and conceptualizing tabular business data) must be implemented.
Additionally, metadata enrichment and management (data cataloging), data governance (data quality and privacy enforcement), and real-time data retrieval are required.
This means complexity, multiple points of failure, and high risk.
These challenges are reflected in a recent K2view survey. Fragmented, hard-to-access data was cited as a major obstacle by most respondents. Solving these data access hurdles is key for organizations aiming to unlock the full power of AI agents, grounded in real, accurate, and secure business information.
Accessing SAP data for MCP clients with K2view
K2view eliminates the complexity of managing multiple MCP servers for SAP and surrounding systems by consolidating data from SAP S/4HANA, ERP modules, HR, finance, and supply chain applications into a single governed data product – exposed through one MCP server. Instead of leaving AI agents to reconcile fragmented and inconsistent data from SAP and non-SAP environments, K2view MCP integration delivers secure, real-time access to harmonized information that is accurate, compliant, and always current. Its patented semantic data layer enriches SAP records with external enterprise data, enforces granular privacy and governance policies, and ensures conversational latency for every query. The result is an SAP MCP deployment that is enterprise-ready, enabling AI agents to provide precise, reliable, and context-rich answers.

By using K2view as a unified MCP server, organizations avoid the inefficiencies and risks of multi-server architectures while simplifying MCP client development and safeguarding both SAP and non-SAP data. Exposing entity-based data through a single MCP server gives AI agents a complete operational context – spanning finance, supply chain, HR, and customer processes – without compromising governance or security. This unified approach accelerates GenAI adoption, ensures regulatory compliance, and equips enterprises to scale AI-powered automation and decision-making confidently across their SAP landscapes.
See how MCP connects
AI chatbots with SAP and enterprise data
MCP Data Integration Product Tour
Take a 15-minute product tour to watch MCP in action. See how an AI chatbot is grounded with live SAP and enterprise data — from text-to-SQL queries, to context-aware reasoning, to secure data fusion — all in real time.
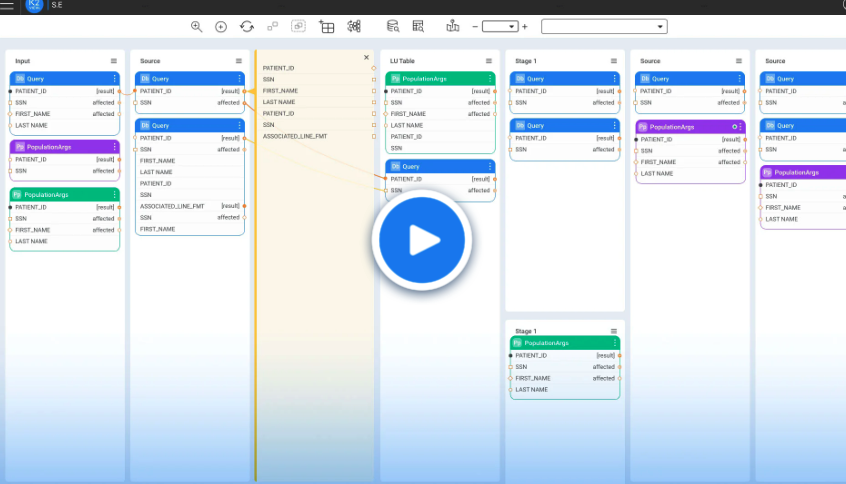
K2view MCP orchestrator workflow and sample code
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of the K2view MCP orchestrator workflow:
- Get the schema for the 'Customer' entity
- Use LLM to translate user query + schema into SQL
- Run the SQL query in the customer's micro-DB context
- Use LLM to convert the SQL result to a user-facing answer
- Return the final answer
The code might look something like this:
orchestrator handleChatbotQuery(input) { |
K2view MCP orchestration provides SAP developers with the following benefits:
- No hardcoding
The logic is fully dynamic and driven by real-time user input and schema. - Live SAP data access
Customer Micro-Databases stay continuously synchronized with SAP S/4HANA. - Orchestrator-based governance
All access is scoped, auditable, and privacy-controlled. - Enterprise-grade flexibility
This same pattern is applicable to any use case simply by changing the schema and user query.
By combining the K2view orchestrator with LLM-powered intent interpretation, SAP developers can unlock conversational AI access to enterprise data with full control, speed, and security – without creating brittle, rule-based logic.
Simplifying SAP MCP integration with K2view
K2view eliminates the complexity of managing multiple MCP servers for SAP and surrounding systems by consolidating AI-ready data from SAP S/4HANA, ERP modules, HR, finance, and supply chain applications into a single governed data product – exposed through one MCP server. Instead of leaving AI agents to reconcile fragmented and inconsistent data from SAP and non-SAP environments, K2view MCP integration delivers secure, real-time access to harmonized information that is accurate, compliant, and always current. Its patented semantic data layer enriches SAP records with external enterprise data, enforces granular privacy and governance policies, and ensures conversational latency for every query. The result is an SAP MCP deployment that is enterprise-ready, enabling AI agents to provide precise, reliable, and context-rich answers.

By using K2view as a unified MCP server, organizations avoid the inefficiencies and risks of multi-server architectures while simplifying MCP client development and safeguarding both SAP and non-SAP data. Exposing entity-based data through a single MCP server gives AI agents a complete operational context – spanning finance, supply chain, HR, and customer processes – without compromising governance or security. This unified approach accelerates GenAI adoption, ensures regulatory compliance, and equips enterprises to scale AI-powered automation and decision-making confidently across their SAP landscapes.
K2view MCP data integration empowers your LLMs with harmonized, business-ready data.